What causes Periods?
Menstrual bleeding, commonly referred to as a period, is a natural and regular part of the menstrual cycle in individuals with a uterus. It involves the shedding of the uterine lining, which occurs approximately once a month in the absence of pregnancy. Menstrual bleeding typically lasts for a few days, although the duration can vary.
The menstrual cycle is controlled by hormonal changes that prepare the body for potential pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the hormone levels drop, signaling the body to shed the thickened uterine lining, resulting in menstrual bleeding. The blood released during menstruation is a combination of blood and tissue from the uterus.
Menstrual bleeding is a normal and healthy process, and its frequency and duration can vary from person to person. It is a crucial aspect of reproductive health and a sign that the reproductive system is functioning as expected.
Also read - Tips to maintain a healthy reproductive system
Tips to maintain good menstrual hygiene
What Causes Spotting?
Spotting can be caused by various factors, and the specific cause can depend on individual circumstances. Here are some common reasons for spotting:
- Hormonal Changes:
- Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can lead to spotting between periods.
- Birth Control: Changes in hormone levels due to birth control methods like pills, patches, or intrauterine devices (IUDs) may cause spotting, especially during the initial months of use.
- Pregnancy:
- Implantation Bleeding: When a fertilized egg implants itself into the uterine lining, it can cause light spotting, known as implantation bleeding.
- Perimenopause and Menopause:
- As a woman approaches menopause, hormonal changes can lead to irregular bleeding, including spotting.
- Infections:
- Infections affecting the reproductive organs, such as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can cause spotting.
- Trauma or Injury:
- Injury to the vaginal or cervical area, for example, during sexual intercourse, may result in spotting.
- Uterine Polyps or Fibroids:
- Non-cancerous growths in the uterus, such as polyps or fibroids, can cause spotting.
- Ovulation:
- Some women may experience spotting around the time of ovulation.
- Medical Conditions:
- Certain medical conditions, such as endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), may lead to abnormal bleeding, including spotting.
- Thyroid Disorders:
- Disorders affecting the thyroid gland can impact menstrual cycles and cause spotting.
- Certain Medications:
- Some medications, like blood thinners or certain antipsychotics, may cause increased bleeding or spotting as a side effect.
Also read - Washing your hair during periods
What is Implantation Bleeding? How is it different from Periods?
Implantation bleeding is a phenomenon that can occur during early pregnancy. It occurs when a fertilized egg, or embryo, attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. This process is called implantation, and it typically takes place about 6-12 days after fertilization. Implantation bleeding is generally light and occurs in the form of spotting, often appearing as pink or brown discharge.
Here are some key differences between implantation bleeding and a regular menstrual period:
- Timing:
- Implantation Bleeding: Typically occurs about 6-12 days after fertilization, which is around the time of the expected menstrual period. It is earlier than a typical period.
- Menstrual Period: Occurs as part of the menstrual cycle, usually about 14 days after ovulation. The timing can vary, but periods generally occur on a regular cycle.
- Flow and Duration:
- Implantation Bleeding: Usually lighter and shorter in duration compared to a regular menstrual period. It may last only a day or two.
- Menstrual Period: Involves a more consistent flow of blood over several days, ranging from 2 to 7 days.
- Color:
- Implantation Bleeding: Often appears as light pink or brown discharge due to the small amount of blood involved and the time it takes to travel from the uterus to the vagina.
- Menstrual Period: Typically involves bright red blood, but the color can vary.
- Consistency:
- Implantation Bleeding: Generally lighter and less consistent than a regular period.
- Menstrual Period: Involves a more consistent and predictable flow.
Also read - How to delay your period?
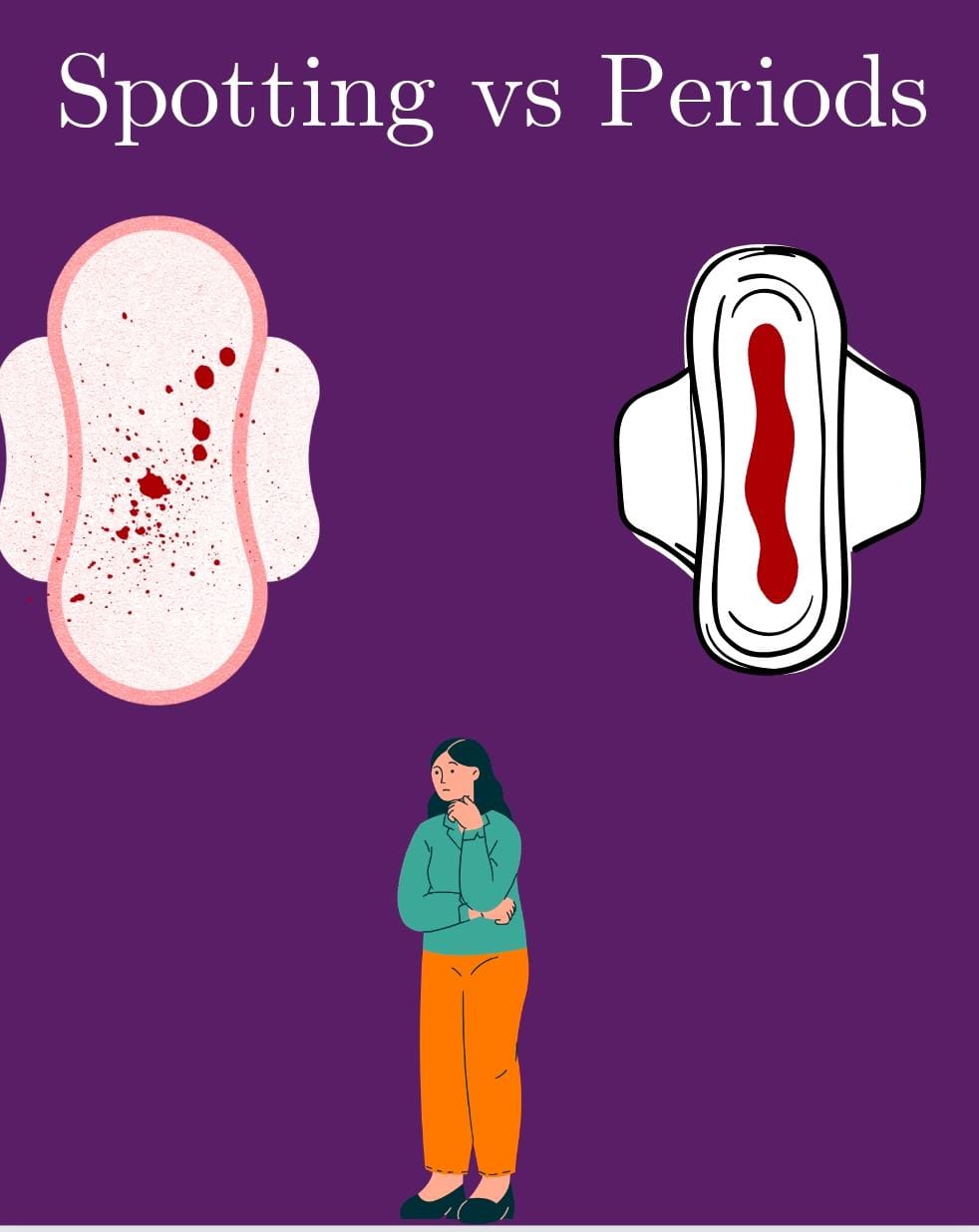
What are some key differences between spotting and periods?
While both spotting and periods involve vaginal bleeding, several key differences distinguish them:
Flow:
- Period: The bleeding is typically heavier, requiring the use of sanitary pads or tampons to manage the flow.
- Spotting: The bleeding is much lighter, often barely noticeable, and doesn't require any sanitary products.
Duration:
- Period: Lasts for several days, usually 5-7 days.
- Spotting: Occurs for a shorter duration, often just a few drops or a light stain lasting a few hours or a day.
Predictability:
- Period: Occurs relatively predictably within a menstrual cycle, often with premenstrual symptoms like breast tenderness or cramping.
- Spotting: This can be more unpredictable, occurring outside of the regular menstrual cycle without any premenstrual symptoms.
Colour:
- Period: Blood may be red, pink, or brown and can vary throughout the period.
- Spotting: Blood is often lighter in colour, typically pink or brown.
Cause:
- Period: Caused by the shedding of the uterine lining due to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle.
- Spotting: Can have various causes, including ovulation, hormonal changes due to stress or illness, birth control methods, implantation bleeding in early pregnancy, or medical conditions like fibroids or polyps.
Remember: If you experience irregular spotting or bleeding, especially outside your usual menstrual cycle, consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Want to learn more about menstrual health? Check out these resources:
- The Federation of Obstetric and Gynaecological Societies of India (FOGSI): https://www.fogsi.org/
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR): https://www.icmr.gov.in/
- Saheli Women's Resource Centre: https://sites.google.com/site/saheliorgsite/
By understanding the difference between spotting and periods, you can better manage your menstrual health and make informed decisions about your body.
When to Consult a Doctor?
Consulting a doctor is important if you experience certain signs or symptoms related to spotting. Here are situations in which you should consider seeking medical advice:
- Heavy or prolonged spotting
- Spotting that occurs regularly or frequently
- Spotting accompanied by severe cramps, fever, or pelvic pain
- Spotting after menopause
Remember, your body is unique, and what's normal for one person might not be for another. If you're concerned about spotting, don't hesitate to talk to your doctor. They can help determine the cause and recommend the best course of treatment.
Also read - Can pads cause irritation?
Read more - Do organic pads help with cramps?